Ancient Egypt holds immense importance in history due to its rich culture, advanced civilization, and lasting legacy. Understanding its history is crucial as it provides insights into the development of early human societies, including advancements in architecture, agriculture, and governance. Moreover, studying Ancient Egypt sheds light on the origins of complex belief systems, such as the worship of multiple gods and the practice of mummification, which significantly influenced later cultures. By delving into its history, we gain a deeper appreciation for the foundations of modern civilization and the enduring impact of Ancient Egyptian achievements.
Early Civilization Along the Nile
Ancient Egypt’s success was largely dependent on the Nile River. It was more than just a river; it was the lifeblood of the civilization, supplying fertile territory for cultivation and supporting the populace. The annual flooding of the Nile deposited nutrient-rich silt on the riverbanks, giving ideal conditions for growing crops such as wheat and barley. This reliable water source also aided transportation and trade, allowing the Egyptians to prosper economically and culturally. Furthermore, the Nile had an important role in religious beliefs and ceremonies, representing abundance and renewal.

The Rise of Pharaohs and Dynasties
The rise of pharaohs marked a significant period in Ancient Egypt, as they were the rulers who held supreme power over the land. Pharaohs were seen as both political leaders and divine figures, believed to be the intermediaries between the gods and the people. They governed with absolute authority, overseeing everything from lawmaking to religious rituals. Pharaohs were often depicted wearing the double crown of Upper and Lower Egypt, symbolizing their control over the entire kingdom. Their reigns were characterized by monumental building projects, such as temples and pyramids, which served as both symbols of their power and tributes to the gods.

Throughout Egyptian history, several dynasties rose and fell, each leaving its mark on the civilization. The Old Kingdom saw the construction of the famous pyramids at Giza, while the Middle Kingdom was known for its expansion of trade and cultural achievements. The New Kingdom marked a period of great prosperity and military conquests, with pharaohs like Hatshepsut and Ramses II leading Egypt to new heights of power and influence. These dynasties contributed to the development of Egyptian art, literature, and architecture, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to fascinate scholars and enthusiasts today.
Ancient Egyptian Society and Culture
Ancient Egyptian society was organized into a hierarchical structure, with different roles and responsibilities for each group. At the top were the pharaohs, who held absolute power and were considered divine rulers. Nobles and priests followed, serving as advisors to the pharaoh and overseeing religious ceremonies. Peasants made up the majority of the population, working the land and contributing to the kingdom’s agricultural success.
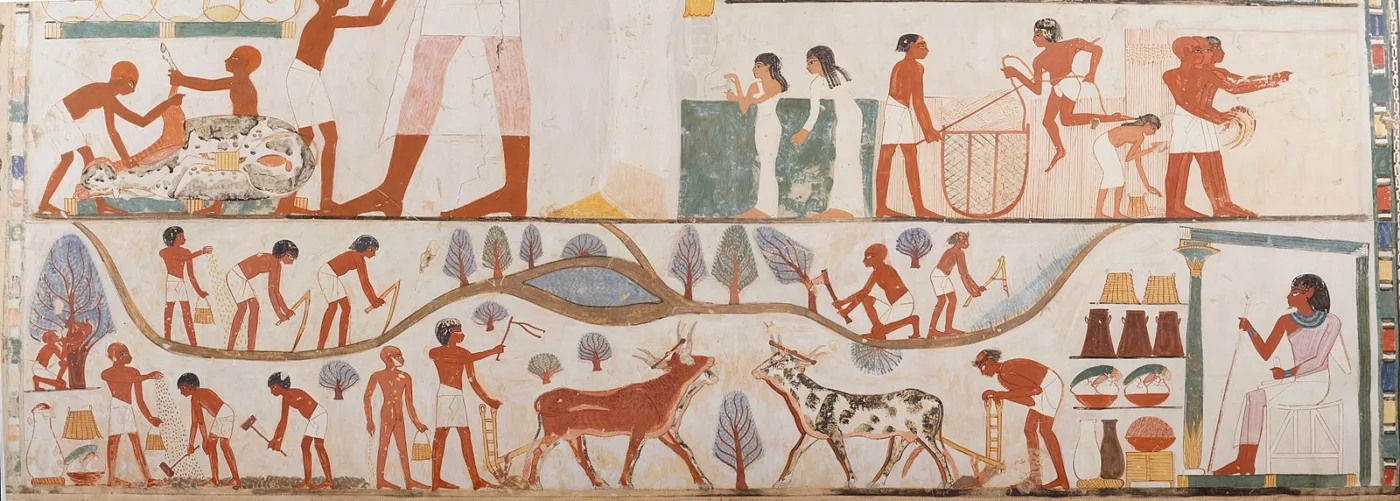

Religion played a central role in Ancient Egyptian life, shaping every aspect of society. Egyptians worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each associated with different aspects of nature and human life. They believed in an afterlife, where the soul would journey to the realm of the dead and be judged by Osiris, the god of the underworld. Daily life revolved around religious rituals and ceremonies, with temples serving as centers of worship and community gatherings. Myths and legends were passed down through generations, providing insight into the Egyptians’ beliefs about the world and their place in it.

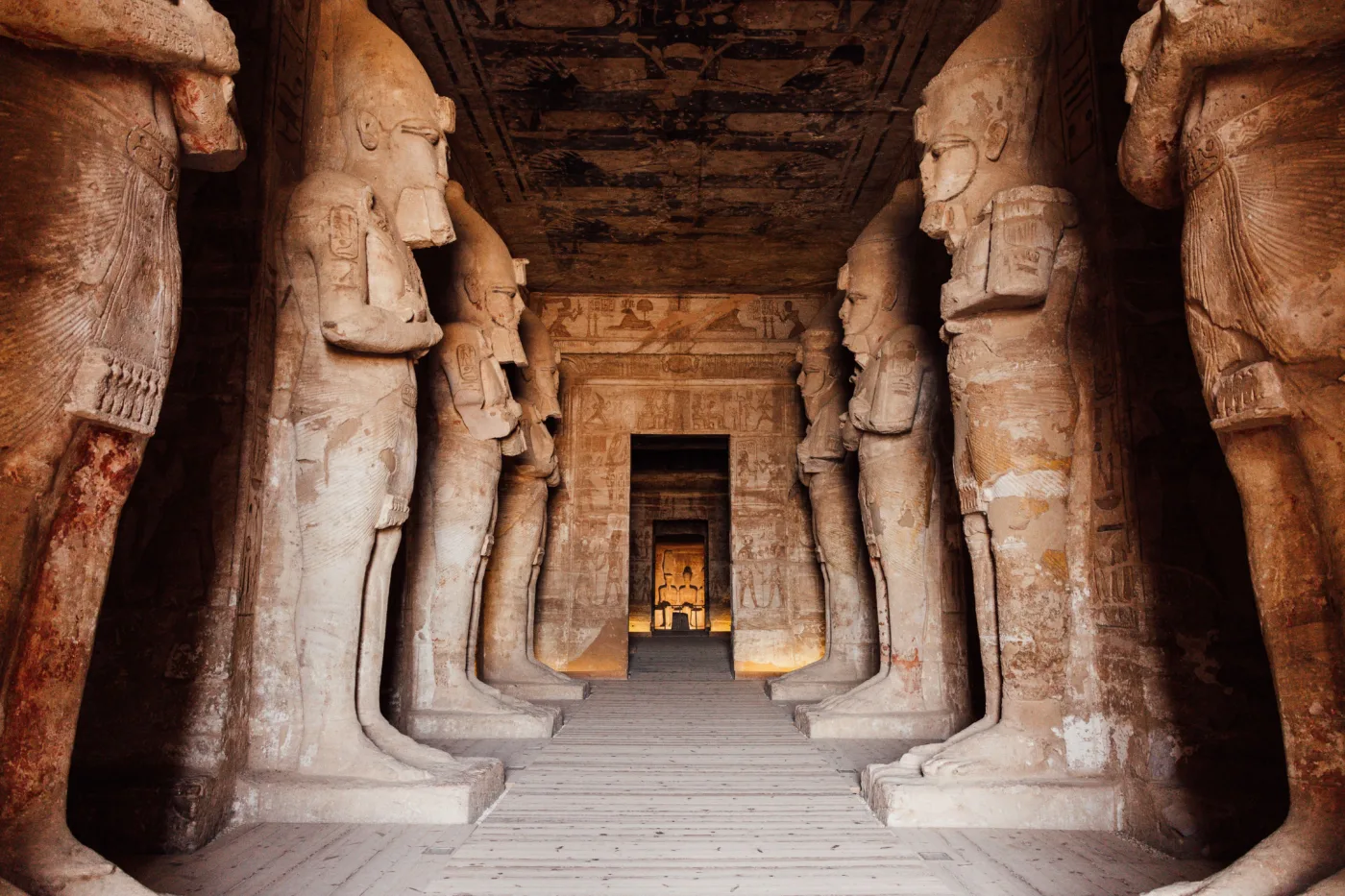
Pyramids and Temples
The iconic pyramids and temples of Ancient Egypt stand as testaments to the ingenuity and grandeur of this ancient civilization. Pyramids, such as those at Giza, were monumental tombs built for pharaohs and their queens. These massive structures were constructed using large limestone blocks, carefully aligned to create perfect geometric shapes. Temples, on the other hand, served as centers of worship and ritual, dedicated to various gods and goddesses. They were adorned with intricate carvings and hieroglyphs, depicting scenes from religious texts and depicting the power of the pharaohs.
Both pyramids and temples held immense significance in Ancient Egyptian society. The pyramids were not only tombs for the pharaohs but also symbols of their divine authority and eternal power. They were constructed to ensure the safe passage of the pharaoh’s soul to the afterlife, equipped with elaborate burial chambers and treasures. Temples, on the other hand, were places of worship and pilgrimage, where priests conducted rituals and ceremonies to honor the gods. The construction of these monumental structures required meticulous planning and skilled labor, with thousands of workers dedicating their lives to these awe-inspiring projects.

Art and Hieroglyphs
Ancient Egyptian art encompassed a variety of forms, showcasing the creativity and craftsmanship of this ancient civilization. Sculpture played a prominent role, with statues of gods, pharaohs, and important figures often carved from stone or wood. These sculptures were characterized by their stylized, idealized forms, conveying power and authority. Painting was another significant art form, with vibrant colors used to decorate tombs, temples, and everyday objects. Jewelry, such as amulets and necklaces, adorned both the living and the deceased, serving as symbols of wealth and status.
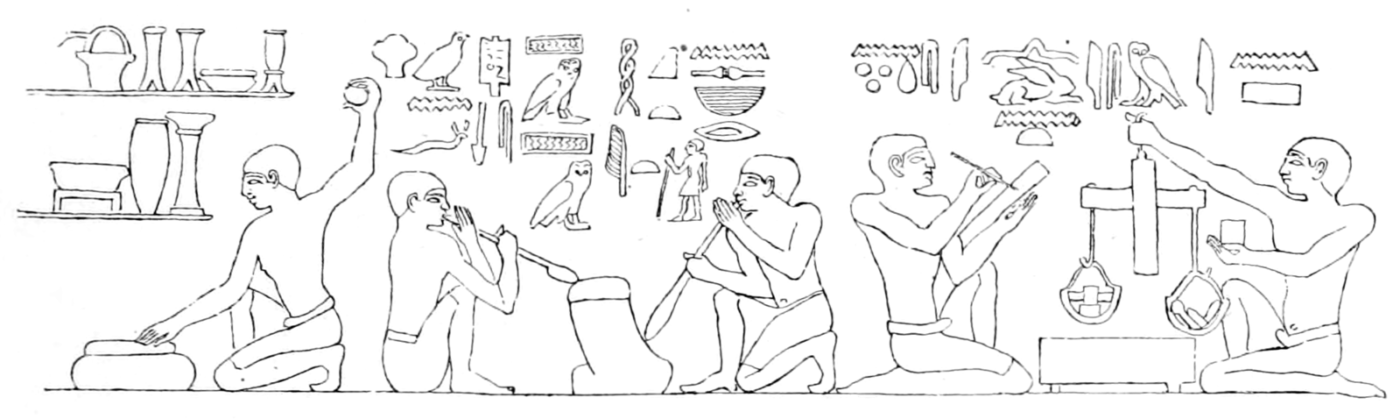
Hieroglyphs were a system of writing used by the Ancient Egyptians, consisting of pictorial symbols that represented objects, sounds, or ideas. They were carved into stone, painted on walls, and inscribed on papyrus scrolls. Hieroglyphs played a crucial role in Ancient Egyptian culture, serving as a means of communication, record-keeping, and religious expression. They were used to write religious texts, historical records, and administrative documents. Understanding hieroglyphs is essential for deciphering the rich history and mythology of Ancient Egypt, as they provide valuable insights into the beliefs, customs, and daily life of this ancient civilization.

Trade and Economy
Ancient Egypt’s economy was primarily agrarian, relying heavily on the fertile land along the Nile River for agriculture. The annual flooding of the Nile deposited nutrient-rich silt onto the riverbanks, creating ideal conditions for growing crops such as wheat, barley, and flax. Agriculture formed the backbone of the economy, providing food for the population and surplus crops for trade. In addition to farming, Ancient Egyptians were skilled craftsmen, producing goods such as pottery, textiles, and jewelry. Craftsmanship thrived in specialized workshops located in cities and villages, contributing to the economic prosperity of the civilization.
Trade played a crucial role in Ancient Egypt’s economy, connecting the kingdom with neighboring regions and distant lands. Ancient Egyptians traded a variety of commodities, including grains, gold, ivory, and precious stones. Trade routes extended across the Mediterranean Sea to regions such as Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Nubia, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth. Along these routes, bustling markets and trading posts emerged, where merchants from different lands converged to exchange goods and ideas. The prosperity of Ancient Egypt’s economy relied on a thriving network of trade routes and economic activities that spanned the ancient world.
Decline and Legacy
The decline of Ancient Egypt can be attributed to various factors, including internal strife, external invasions, and environmental changes. Internal conflicts, such as power struggles among the ruling elite and economic instability, weakened the centralized authority of the pharaohs. External threats, such as invasions by foreign powers like the Assyrians and Persians, further destabilized the kingdom. Additionally, environmental factors, such as droughts and floods, contributed to agricultural failures and food shortages, exacerbating social unrest. Over time, these combined pressures led to the gradual decline of Ancient Egypt as a dominant civilization in the region.
Despite its decline, Ancient Egypt left a profound and enduring legacy on world history and culture. Its contributions to art, architecture, science, and religion continue to influence and inspire people around the globe. The monumental architecture of the pyramids and temples, the intricate hieroglyphic writing system, and the advancements in medicine and mathematics all attest to the ingenuity and creativity of this ancient civilization. Ancient Egypt’s rich mythology and religious beliefs have had a lasting impact on global culture, shaping the development of literature, art, and spirituality throughout history. The legacy of Ancient Egypt serves as a testament to the enduring power and influence of one of the world’s greatest civilizations.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of Ancient Egypt, I encourage you to continue delving into the wonders of this captivating civilization. There are endless mysteries to uncover, from the secrets of the pyramids to the intricacies of hieroglyphic writing. By further exploring Ancient Egypt’s history, art, and culture, you can gain a deeper understanding of its profound influence on the world. Whether through books, museums, or online resources, the legacy of Ancient Egypt awaits your discovery, offering insights into the enduring legacy of one of humanity’s greatest civilizations.
More of → Ancient Civilizations ←
FAQ
1. What were the major achievements of Ancient Egypt?
Ancient Egypt made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and architecture. They invented hieroglyphic writing, developed a complex calendar, and built monumental structures like the pyramids.
2. How were pharaohs regarded in Ancient Egypt?
Pharaohs were revered as divine rulers with absolute authority over the land and its people. They were believed to be intermediaries between the gods and the mortal realm, responsible for maintaining order and harmony.
3. What led to the decline of Ancient Egypt?
Several factors contributed to the decline of Ancient Egypt, including foreign invasions, internal conflicts, environmental degradation, and economic decline. The conquests of foreign powers and the loss of traditional values hastened its demise.
4. Why were the pyramids built?
The pyramids served as monumental tombs for pharaohs and their families, designed to safeguard their remains for eternity and ensure their successful transition to the afterlife. They also symbolized the pharaoh’s divine power and eternal rule.
5. How did Ancient Egyptian religion influence daily life?
Religion permeated every aspect of Ancient Egyptian society, guiding social, political, and economic practices. Rituals, offerings, and ceremonies were conducted to appease the gods, ensure fertility, and maintain cosmic order.



