Curious about the legendary beginnings of Rome? The founding of Rome is a tale steeped in myth and history. Let’s delve into the captivating origins of this ancient city and uncover the stories that have shaped its legacy.
Brief Overview of the Myth of Romulus and Remus
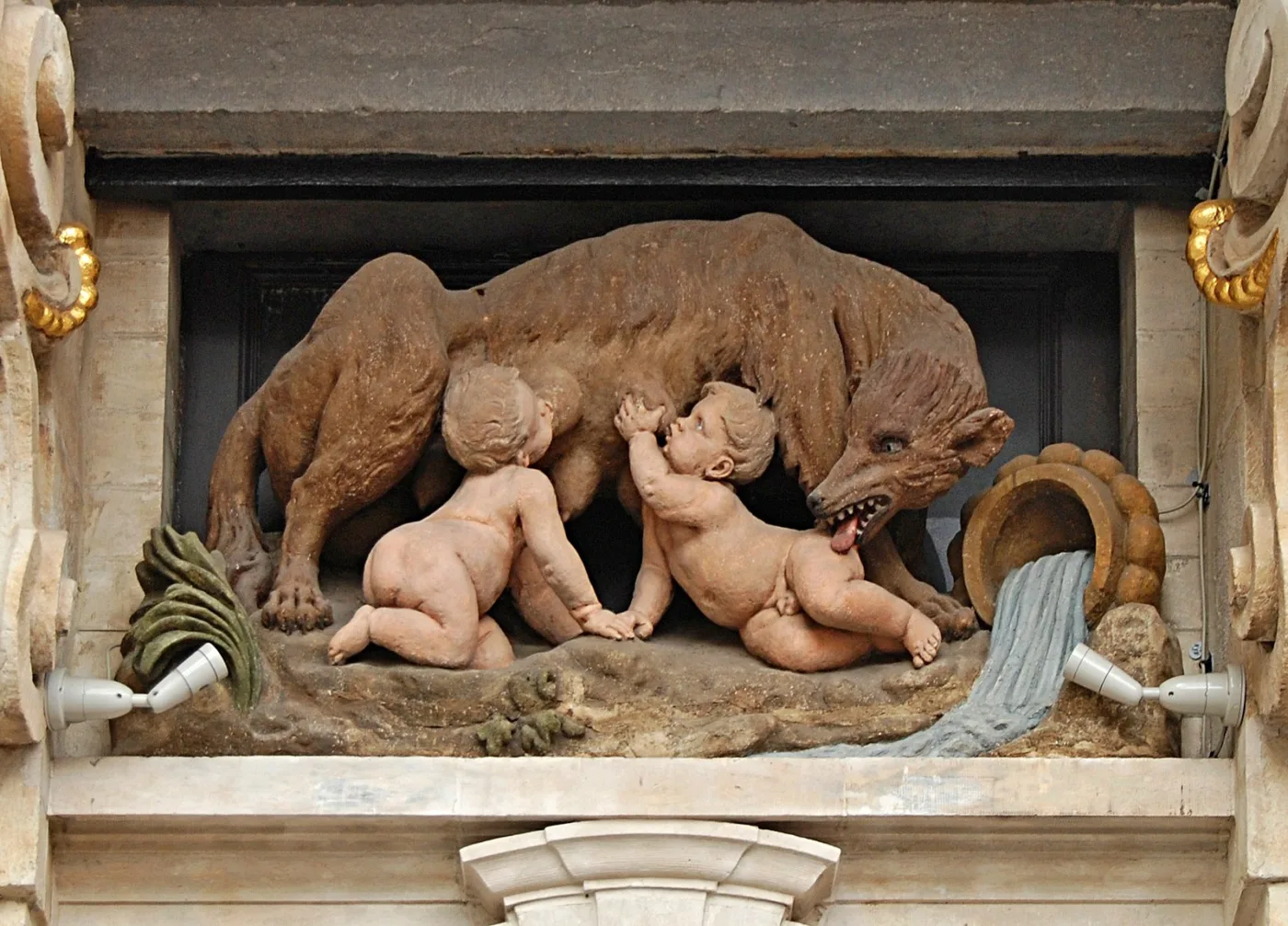
According to the traditional myth, Rome’s founding is intertwined with the legendary tale of Romulus and Remus. Born to a Vestal Virgin and the god Mars, these twins were abandoned and raised by a she-wolf before founding Rome. This myth has long been ingrained in Roman culture, shaping how many perceive the city’s beginnings.
However, beyond the myth lies a rich tapestry of historical debate. Scholars, archaeologists, and historians have long grappled with piecing together the true origins of Rome. Through archaeological digs, analysis of ancient texts, and interdisciplinary research, they seek to separate fact from fiction and uncover the real events that led to the founding of Rome.

Pre-Roman Settlements and Early Civilization
Overview of Pre-Roman Settlements
Before Rome’s ascent, the region was home to diverse settlements, each with its own unique identity and way of life. These settlements dotted the landscape, ranging from small villages to bustling towns, and they played a crucial role in shaping the early history of the area. Archaeological excavations have unearthed evidence of these pre-Roman settlements, revealing traces of ancient dwellings, tools, pottery, and other artifacts. Through careful analysis, historians piece together the daily lives, customs, and interactions of the people who inhabited these communities.
The region’s geography and natural resources influenced the location and development of these settlements. Rivers provided water for agriculture and transportation, while fertile plains supported farming and trade. Mountains offered protection and resources, shaping settlement patterns and defense strategies. The interactions between these settlements were complex and multifaceted. Trade networks crisscrossed the region, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. Alliances were forged, conflicts arose, and cultures intermingled, leaving a rich tapestry of influences on the evolving social and political landscape.
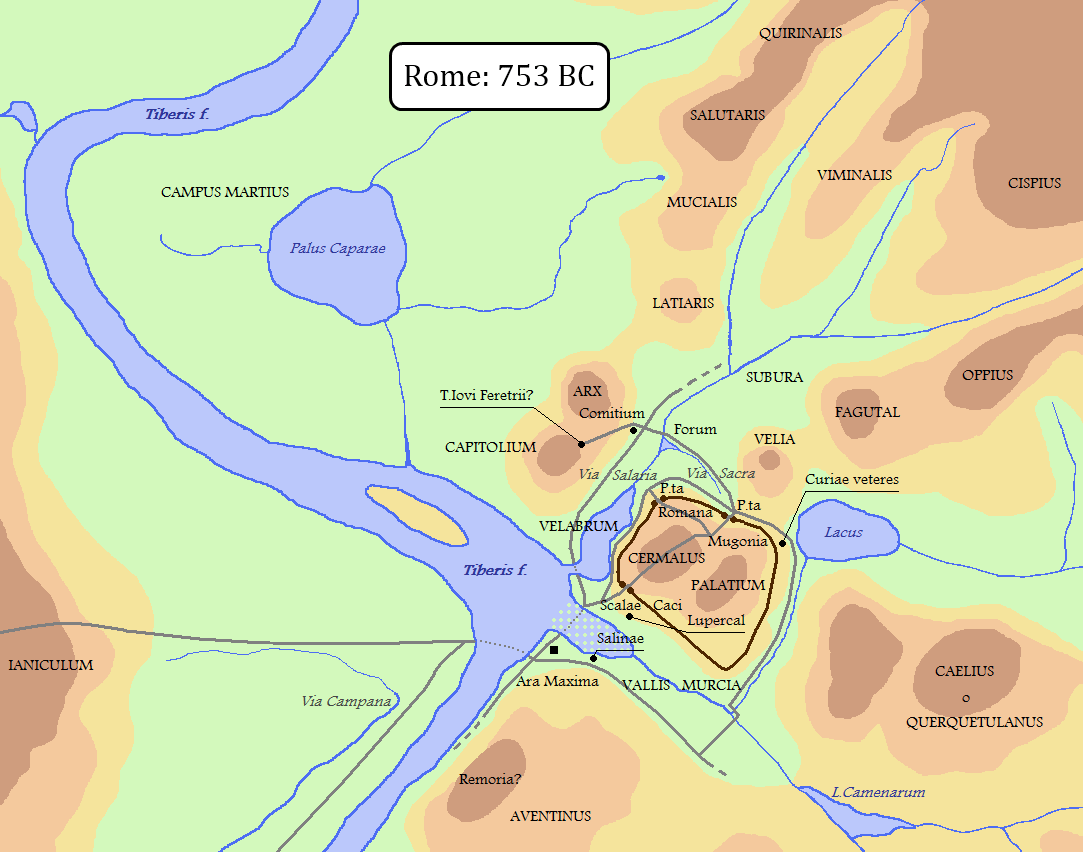
Social, Economic, and Cultural Landscape of Early Inhabitants
Before Rome’s dominance, life was vastly different yet surprisingly similar to our own. Early inhabitants lived in communities, forming social bonds based on kinship, trade, and shared beliefs. Social structures varied among these communities. Some were hierarchical, with leaders or chiefs guiding decision-making and resolving disputes. Others were more egalitarian, with decisions made collectively by the community.
Economic activities were essential for survival and prosperity. Agriculture formed the backbone of the economy, with farmers cultivating crops such as wheat, barley, and grapes. Livestock farming, including raising sheep, goats, and cattle, also played a significant role in providing food and resources. Trade was another crucial aspect of the economy. Communities exchanged surplus goods with neighboring settlements, fostering connections and facilitating the exchange of ideas and technologies. Trade routes crisscrossed the region, linking distant communities and contributing to economic growth.
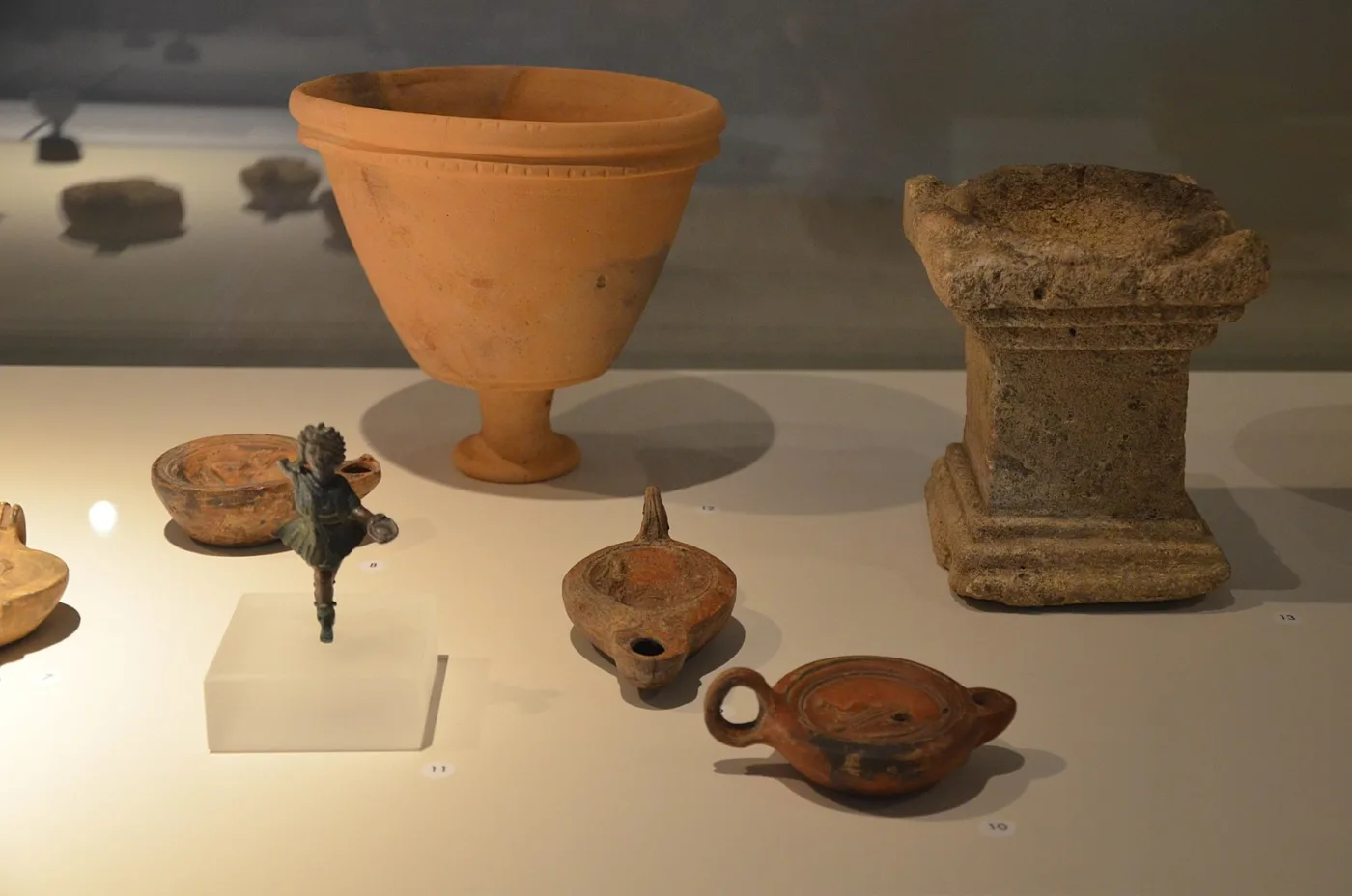

Cultural practices reflected the diversity of early inhabitants’ beliefs and traditions. Rituals and ceremonies celebrated important events such as births, marriages, and harvests, while religious beliefs shaped daily life and provided explanations for natural phenomena. Art and craftsmanship flourished, with skilled artisans producing pottery, textiles, and tools. These artifacts not only served practical purposes but also reflected the creativity and ingenuity of early societies.
Etruscan Influence and Urban Development
Etruscan Civilization’s Impact on Early Rome
The Etruscans, an ancient civilization that thrived in central Italy before the rise of Rome, left an indelible mark on the development of the Eternal City. Their influence extended across various aspects of Roman life, from religion and politics to art and architecture. Etruscans introduced new techniques in urban planning and architecture, transforming Rome from a collection of settlements into a thriving city. They pioneered the use of arches, vaults, and aqueducts, revolutionizing construction methods and laying the groundwork for Rome’s iconic architectural legacy.

Urban Development and Infrastructure
The Etruscans played a pivotal role in the development of Rome’s infrastructure, constructing roads, bridges, and drainage systems that facilitated trade and communication. These improvements not only enhanced the city’s functionality but also contributed to its growth and prosperity. Etruscan influence extended beyond physical infrastructure to the organization of urban space. They introduced concepts of city planning, dividing Rome into distinct districts and establishing public spaces such as forums and marketplaces that served as centers of social and economic activity.
Etruscan Contributions to Roman Society and Culture
In addition to their architectural and engineering achievements, the Etruscans made significant contributions to Roman society and culture. They influenced Roman religious practices, introducing deities, rituals, and divination techniques that became integral to Roman spirituality. Etruscans also left their mark on Roman art, inspiring new artistic styles and techniques that blended with indigenous Roman traditions. Their influence can be seen in everything from pottery and sculpture to murals and frescoes, enriching the visual landscape of ancient Rome.

Rise of the Roman Republic
From a Collection of Settlements to a City-State
Rome’s journey from humble beginnings to a powerful city-state was a gradual process marked by significant milestones. Initially, Rome consisted of small settlements scattered across the seven hills along the Tiber River. Over time, these settlements grew and merged, forming a cohesive urban center.
The consolidation of power and resources within Rome’s walls laid the foundation for its transformation into a city-state. As Rome expanded its territory through conquest and diplomacy, its influence spread, solidifying its position as a dominant force in central Italy.
Factors Shaping Rome’s Growth
Numerous factors contributed to Rome’s rise, including its strategic location, robust economy, and strong military. The city’s location on the Tiber River provided access to trade routes and fertile land for agriculture, fostering economic prosperity and growth.
Politically, Rome underwent a series of transformations, transitioning from a monarchy to a republic. The overthrow of the last Etruscan king paved the way for a new form of government based on a system of checks and balances, with power distributed among elected officials known as senators and magistrates.
The Roman Republic’s military prowess was another key factor in its rise to prominence. Rome’s legions, comprised of citizen-soldiers drawn from all walks of life, were disciplined, well-trained, and highly effective in battle. Through a combination of conquest and diplomacy, Rome expanded its territory, securing its position as a dominant power in the Mediterranean.
Establishment of the Roman Republic and Its Governance
The establishment of the Roman Republic marked a significant turning point in Rome’s history. Under this new system, power was vested in elected officials who represented the interests of the people. The Republic was governed by a complex system of laws and institutions, including the Senate, the Assembly, and the Magistrates, which ensured accountability and balance of power.
Through a series of reforms and conflicts, the Roman Republic evolved and adapted to the changing needs of its citizens. Despite internal strife and external threats, the Republic endured for centuries, leaving a lasting legacy of democracy and governance that continues to influence political systems around the world.
Myth vs. Reality: The Romulus and Remus Story
Comparison
The traditional myth of Romulus and Remus, born of a Vestal Virgin and the god Mars, has long been ingrained in Roman culture. According to legend, the twins were abandoned and raised by a she-wolf before founding Rome. However, when we compare this myth with historical evidence, we find discrepancies and inconsistencies.
Exploration of Different Theories
Scholars and historians have proposed various theories and interpretations to explain the origins of Rome. Some suggest that Rome’s founding was a gradual process, shaped by the convergence of different cultures and communities. Others argue that the Romulus and Remus story is a mythological embellishment of historical events, designed to glorify Rome’s past and legitimize its authority.

Political and Cultural Significance of the Romulus and Remus Legend
Regardless of its historical accuracy, the Romulus and Remus legend holds immense political and cultural significance for Rome. It served as a powerful symbol of divine favor and the right to rule, bolstering the authority of the ruling elite. The myth also provided a narrative framework for understanding Rome’s origins and identity, shaping how Romans viewed themselves and their place in the world.
Rome’s Founding
Rome’s Lasting Influence on Western Civilization
Rome’s influence on Western civilization is undeniable, with its legacy reverberating through the centuries. The Roman Empire’s expansive reach and enduring institutions laid the groundwork for modern society, shaping everything from governance and law to language and culture.
Rome’s Impact on Law, Politics, Art, Architecture, and Culture
Rome’s contributions to law, politics, art, architecture, and culture have left an indelible mark on the world. Roman law, with its emphasis on justice and equity, laid the foundation for modern legal systems. Roman political institutions, such as the Senate and the concept of citizenship, continue to inform democratic governance today.

In the realm of art and architecture, Rome’s innovations in engineering and design continue to inspire awe and admiration. From the grandeur of the Colosseum to the beauty of the Pantheon, Roman architecture showcases the ingenuity and ambition of the ancient world.
Roman culture, with its rich tapestry of myths, legends, and traditions, has also left a lasting imprint on Western culture. The ideals of honor, duty, and virtue espoused by Roman philosophers and writers continue to resonate with audiences worldwide.
More of → Ancient Civilizations ←
FAQ
1. What are some theories surrounding the founding of Rome that diverge from the myth of Romulus and Remus?
Beyond the myth of Romulus and Remus, various theories exist regarding the founding of Rome. Some scholars propose that Rome’s origins are rooted in a gradual process of settlement and cultural assimilation, while others suggest that it may have been founded by an amalgamation of indigenous tribes. These theories challenge the traditional narrative, prompting further exploration into Rome’s complex history.
2. Who were Romulus and Remus, and how are they connected to the founding of Rome?
Romulus and Remus are central figures in the founding myth of Rome. As the legendary founders of the city, their story symbolizes Rome’s divine origins and its status as a destined world power. Despite their mythical origins, their tale continues to shape Rome’s cultural identity.
3. What role did the Etruscans play in the founding of Rome?
The Etruscans, an ancient civilization that predated Rome, played a significant role in shaping the city’s early development. Their influence can be seen in Rome’s architectural and urban planning, as well as its religious and cultural practices. The Etruscans laid the groundwork for Rome’s emergence as a dominant force in the region.
4. Can archaeological evidence shed light on the founding of Rome?
Archaeological evidence offers valuable insights into the founding of Rome, providing a glimpse into the lives of its early inhabitants and the evolution of the city over time. Excavations have uncovered artifacts, structures, and settlements that shed light on Rome’s prehistoric past and the factors that led to its establishment.
5. How did the founding of Rome influence the development of Western civilization?
The founding of Rome marked the beginning of a civilization that would profoundly influence the course of Western history. As Rome expanded its territory and established its dominance in the Mediterranean world, it spread its language, laws, and culture across vast regions. Roman innovations in governance, engineering, and the arts laid the groundwork for modern society, shaping everything from political institutions to architectural styles. Rome’s legacy as a cultural and political powerhouse continues to resonate in the modern world.



